

H 2 (g) requires a 1.5 V overpotential, while Pt (s) requires 0 V overpotential This case happens more frequently with gases. An overpotential or voltage excess is sometimes needed to overcome interactions at the electrode surface.Oxidation occurs at the anode in an electrolyte cell.
#Anode vs cathode series
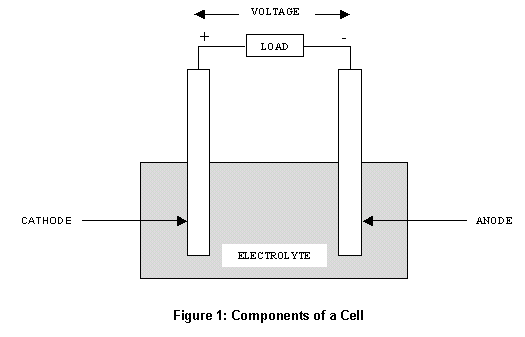
It is important to use a resistor in series with supply voltage otherwise, the circuit can be damaged due to over-current. Depending upon the logic, the corresponding 0V is given which power-ups the diode and light is emitted from it. The cathode is the terminal where electricity leaves the device. In common anode type, the common voltage of +5V is applied to all the diodes. Zinc behaves as the anode (supplying electrons) of the galvanic cell and the copper as the. But grid swing will be about 1.1200Vpk or 220V peak. Main Differences between Anode and Cathode The anode is the terminal where electricity enters the device. In closed circuit, a current flows between the two electrodes. Distortion of the CF alone is about 50.1 0.5, nice. This will come out about 0.9 for many cases. There are four primary factors that determine whether or not electrolysis will take place even if the external voltage exceeds the calculated amount: THD at large power will be around 5 divided by the feedback factor. If an aqueous solution of sodium chloride were used in the above system, hydrogen would undergo reduction instead of sodium, because it is a stronger oxidizing agent that sodium. The anode is the negative side and the cathode is the positive side. The odd part is that the signs on the cathode and anode in an electrolytic cell are the opposite way, the cathode is negative (-), and the anode is positive. In electrochemistry, electrons flow the opposite way. The substance that is the strongest oxidizing agent will be reduced. In general, the anode is the positive side and the cathode is the negative side. The substance that is the strongest reducing agent (the substance with the highest standard cell potential value in the table) will undergo oxidation. The conditions under which the electrolyte cell operates are very important.Anode is now positive charged and the cathode has a negative charged. Note that the site of oxidation is still the anode and the site of reduction is still the cathode, but the charge on these two electrodes are reversed. the charge of anode and cathode are positive and negative in an electrolytic cell and in the galvanic cell it is the opposite.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
